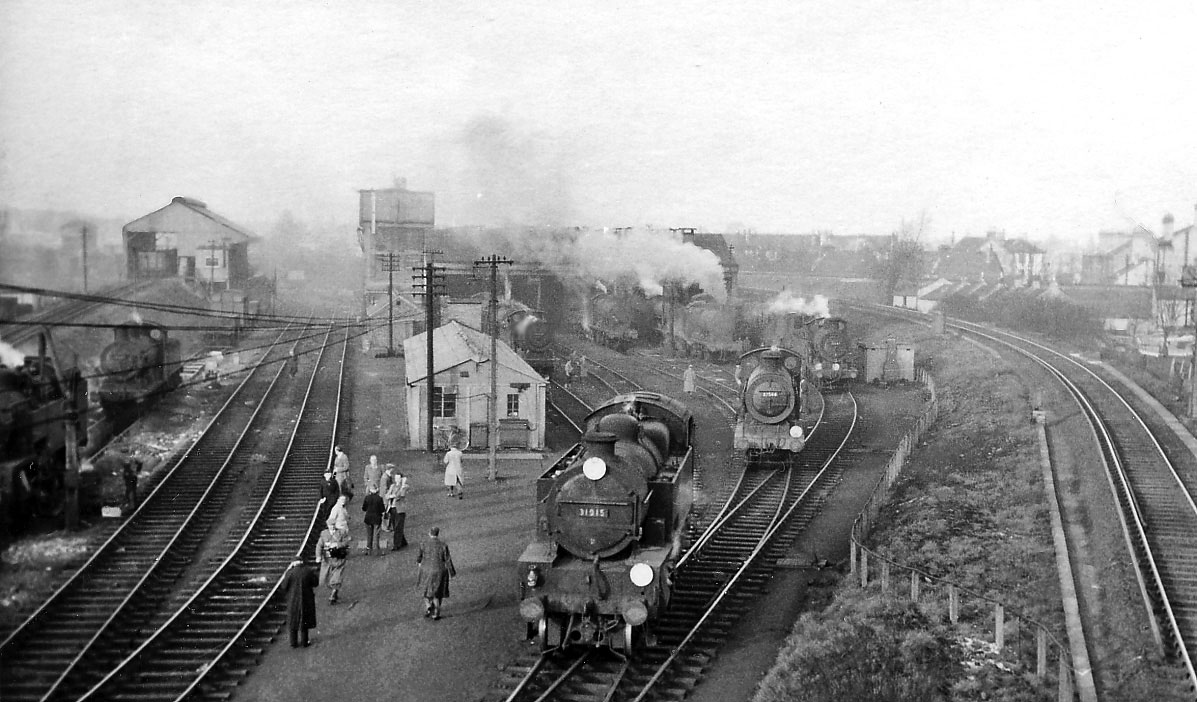• Click on images to enlarge

Arthur Conan Doyle
Medieval Norwood
Norwood was originally in Surrey. It was part of the Great North Wood (hence later Norwood) which stretched from Croydon to Camberwell.
1086 The Great North Wood within the parish of Croydon recorded in the
Domesday Book. The land belonged to the Archbishop of Canterbury, although the local Lord of the Manor held hunting and tree-felling rights, and local people kept pigs in the wood.
C12 First reference to Norwood.
C14 Whitehorse family held land in area (hence Whitehorse Road and Whitehorse Lane.
1464 Bailiff’s account of the Chauntry of St. Nicholas mentioned a rent of 33s 4d paid annually for a place called Chelmerden (or Shelverdine). It was a coppice of woodland later named Goat House in the area now called Sunnybank.
Stuart Norwood
1678 Goat House (see 1464) first appeared on a map of the Archbishop of Canterbury’s lands in the area by William Mar.
Georgian Norwood
1798 Pascall’s Brickworks founded by Henry Pascall Senior (1753 - 1829). Located (later?) at on the junction of the bottom of South Norwood Hill and Penge Road. Used the 1911 canal and later railway to mob=ve the bricks.
1792-1802 Croydon Enclosure Acts lead to disappearance of common land in Norwood.
1800 Topographical Map Of The Country Twenty Miles Round London. Croydon Canal shown plus Goat House (clearing/farmhouse).
Regency Norwood
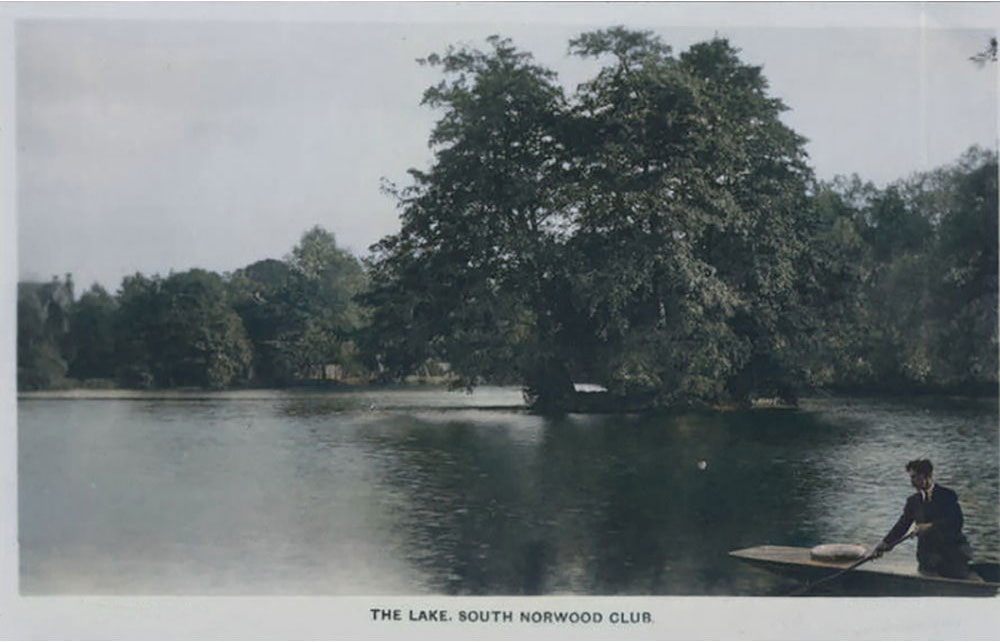
1809 Croydon Canal opened, built by John Rennie. It linked Surrey Docks with West Croydon). Reservoir for canal built (now South Norwood Lake).
1810 The first public building in South Norwood was a public house at 64 High Street (later named Jolly Sailor).
South Norwood consisted of brickworks and farmland at the time.
1836 Croydon Canal closed and drained.
Early Victorian South Norwood
1839 Railway station opened in Norwood on London & Croydon Railway opened Railway built on site of old Croydon Canal. Station now Norwood Junction) initially called Jolly Sailor.
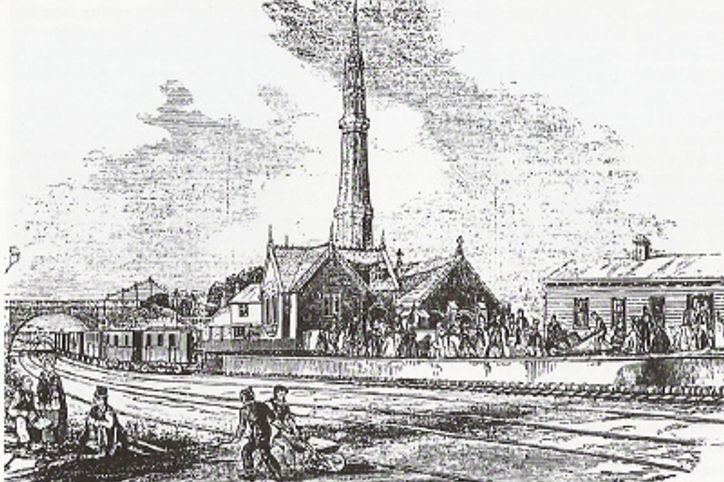
1845 Experimental atmospheric railway built along new railway. Pumping station added.
1846 Jolly Sailor Railway station renamed Norwood Station.
Area became known as South Norwood.
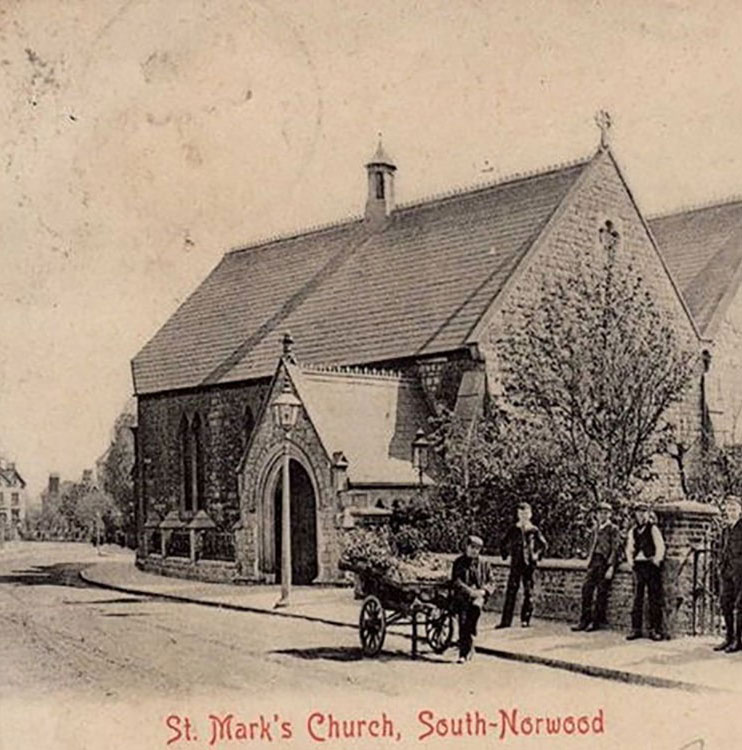
1852 St Mark’s Church (C of E) opened on Albert Road. Architect unknown.
1853 The Ship opened at 55 High Street.
1854 Crystal Palace exhibition building was moved from Hyde Park to Sydenham Hill
c.1855 Railway Signal pub opened at 1 Portland Road.
Albert Road listed. One of South Norwood earliest roads.
1856 Norwood Station renamed Norwood Junction.
The Joiners Arms opened at 50-52 Woodside Green.
1856 Norwood Junction station moved and expanded to incorporate seven tracks.
Mid Victorian South Norwood
1860s Jolly Sailor pub rebuilt.
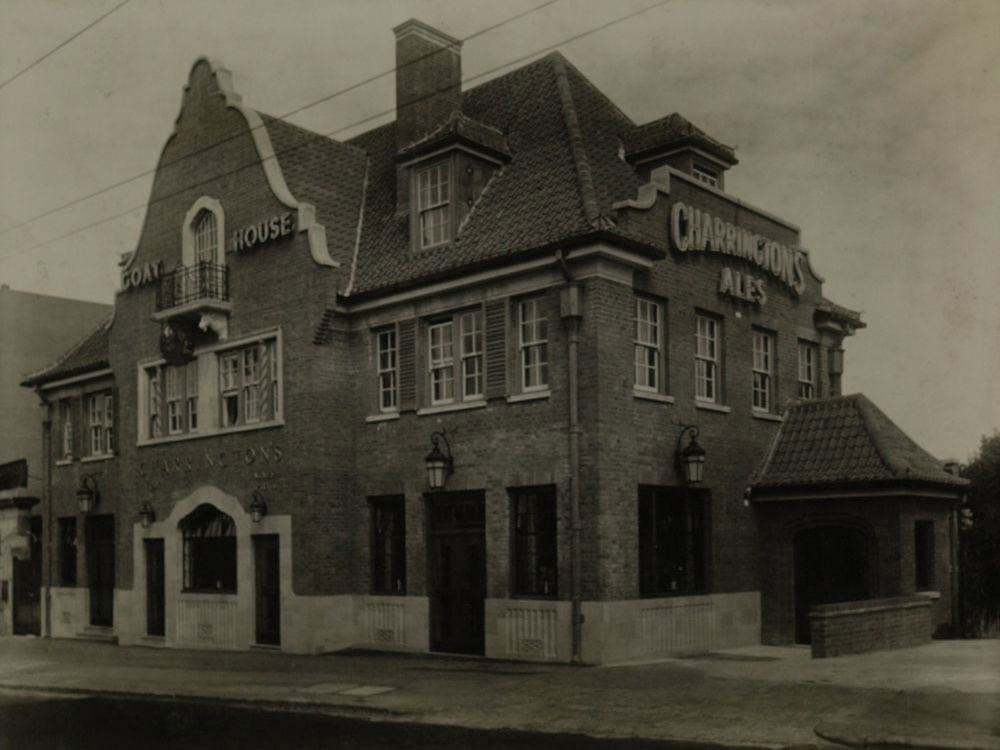
Goat House Hotel at 2 Penge Road rebuilt. Bridge nearby named Goat House Bridge.
1866 Prince of Denmark pub opened at 152 Portland Road (now Portland Arms).
South Norwood Irrigation Farm opened. Designed by Baldwin Latham (1836-1917), surveyor to Croydon Board of Health. It closed in 1967 (now a park).
1867 The Albion opened at 26 High Street. Built on the corner site of Pascall’s brickfields.
1869 The Albert Tavern opened on Harrington Road.
1870 The Gladstone opened at 167 Portland Road.
1875 William Stanley (1829-1909) opened a factory in Belgrave Road.
Late Victorian South Norwood
1880s Horris Brickworks opened in Woodside (now Brickfields Park). Led to 20 pubs in area.
1881 The Norwood Sports Club formed and the old canal reservoir used for fishing, swimming and skating in winter.
1887 Metropolitan Cattle Trough and Drinking Fountain added to 25 South Norwood Hill.
1889 South Norwood Recreation Ground opened (14 acres) with entrances in Selhurst Road, Tennison Road and Cargreen Road. It originally had a bandstand and was planted with a boundary of trees; a bowling green, pavilion and football pitches wereadded later.
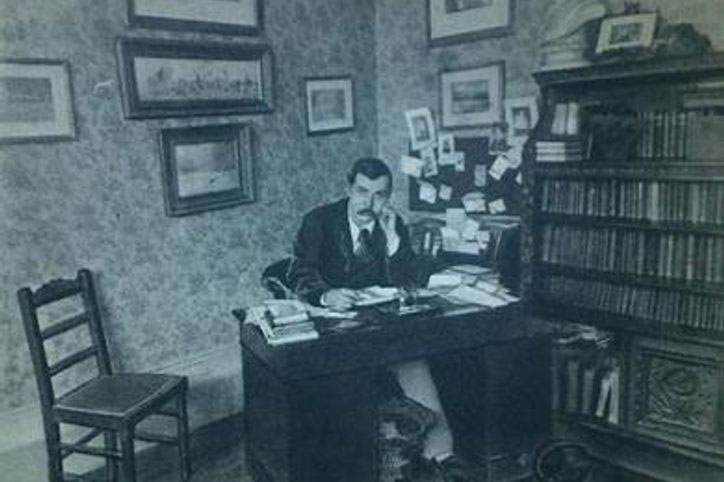
1891-4 Arthur Conan-Doyle (1859–1930) lived at 12 Tennison Road, He wrote the first Sherlock Holmes novels there. Photographed in his study.

1895 Holy Innocents’ Church opened in Selhurst Road by the new Recreation Ground. Architect: George Frederick Bodley (1827-1907). Grade II listed.
Edwardian South Norwood
1900 Composer Samuel Coleridge Taylor (1875-1912) lived at 30 Dagnall Park.
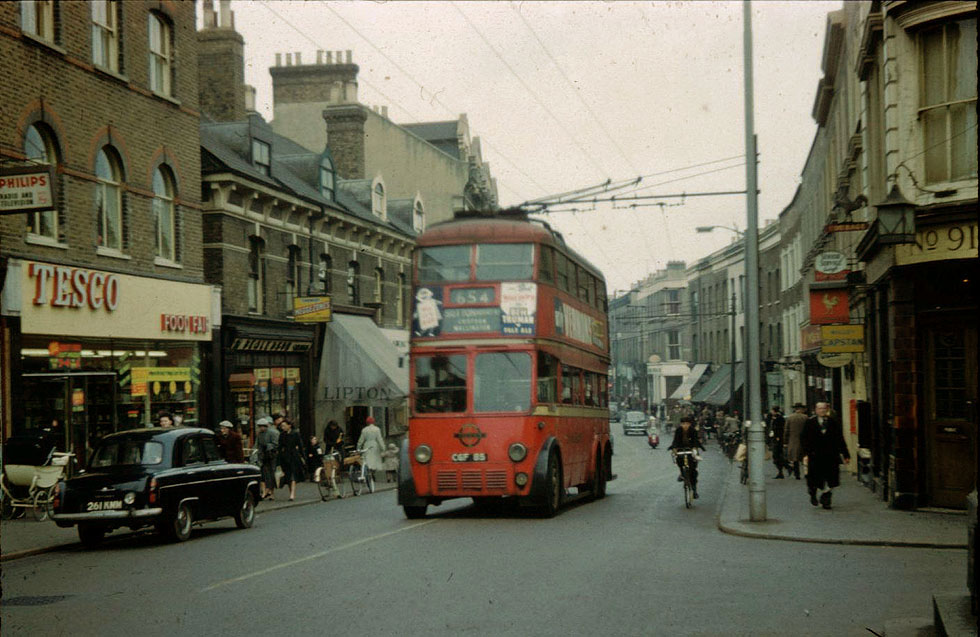
c. 1903 Trolley buses introduced.
1903 Stanley Halls community arts centre opened.
1906 Congregationalist church opened on Enmore Road.
1907 Stanley Trade Technical School for Boys built and designed by William Stanley at 12 South Norwood Hill. It was the first technical trade school in the country.
Clock tower erected by “the people of South Norwood to commemorate the Golden Wedding anniversary of Mr and Mrs W F Stanley”
1909 Stanley Halls community arts centre completed.
William Stanley died.
1910 Horris Brickworks acquired by Edward Handley, Seven chimneys on site (now Brickmeadows Park & Lake). Two chimneys were over 160 feet high. More info
1911 New Electric Theatre opened at 448 Portland Road. 300 seats.
c. 1911 Central Hall Picture Palace opened at 110 Portland Road.. It seated 500 on two tiers.
1915 Horris Brickworks (silent film) purchased by Edward Handley (renamed Woodside Brickworks in 1947).
Interwar South Norwood
1921 New Gaiety Cinematograph Theatre opened at 45 High Street (later Astoria). 750 seats in stalls and a small circle.
1922 War Memorial added at Holy Innocents’ Church in Selhurst Road.
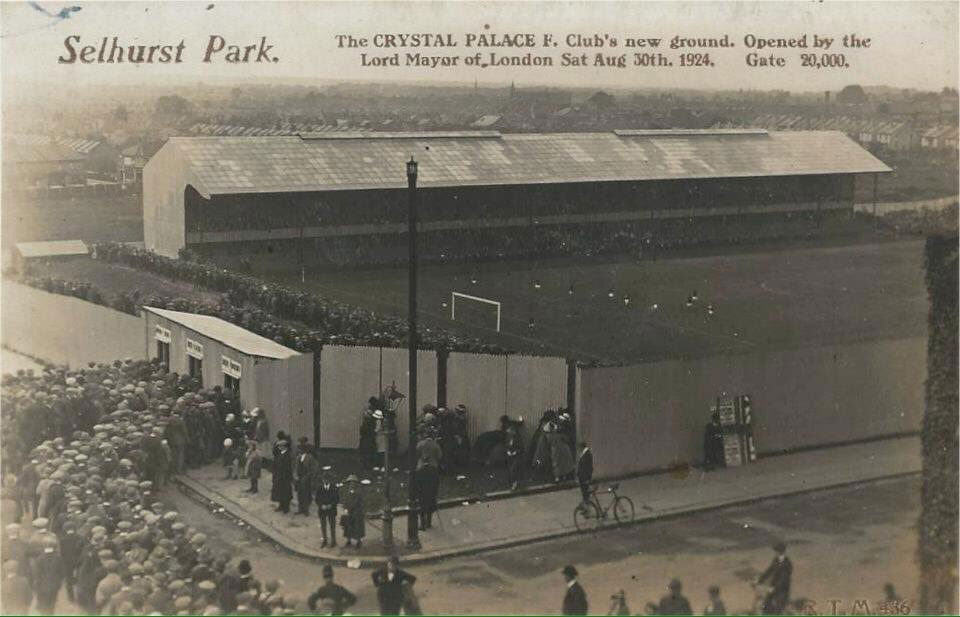
1924 Crystal Palace FC new stadium at Selhurst Park, Whitehorse Lane, opened. Designed by Archibald Leitch (1865-1939). Previously the site was a brickworks.
1926 William Stanley factory moved to New Eltham.
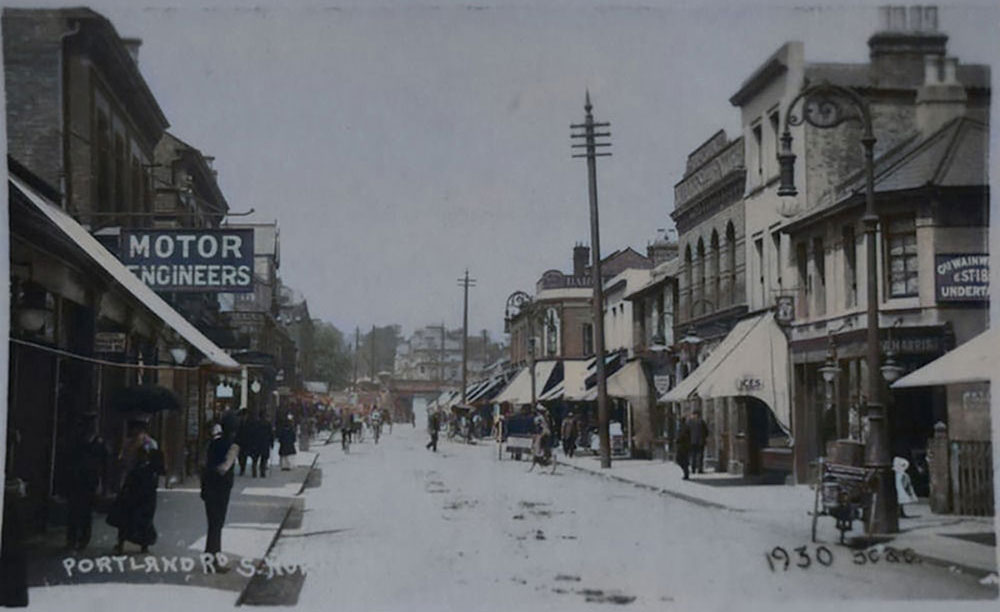
1930 Photograph of Portland Road.
1931 Croydon Corporation purchased 16 acres of the sports ground but the club continued to lease the facilities. The lake and surrounds were opened to the public.
1933 St. Chad’s Church (RC) opened on Whitworth Road.
1935 Regent Cinema (ex-Electric) closed down.
1936 Film of Selhurst Park football ground (0:41)
Goat House Hotel at 2-4 Penge Road rebuilt.
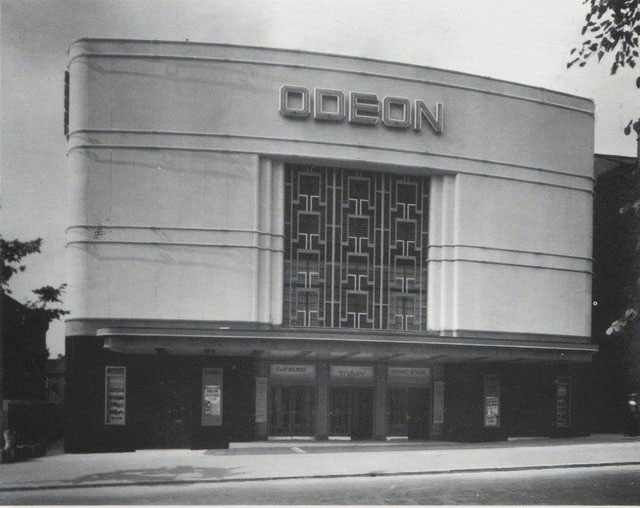
1937 Odeon South Norwood opened at 18-22 Station Road. Designed by Andrew Mather (1891-1938) with 1,020 seats in the stalls & 552 in the circle.
New Gaiety Cinematograph modernised by architect Richard Seifert (1910-2001) in an Art Deco style, and re-named Astoria Cinema.
WW2 & South Norwood
1940 Film (0:20) of removal of signs including Norwood Junction during the Second World War. Also view of Goat House pub.
1940-1941 South Norwood heavily bombed by German airforce (more info).
Handley Brickworks (later Woodside) closed down to become a staging post for troops of the Canadian Army prior to the invasion of France.
1944-1945 German V1 Flying Bombs caused much death & destruction in South Norwood.
July 1944: Albert Tavern in Harrington Road destroyed by a V1.
Oct 1944 Only one V2 Flying bomb struck South Norwood (witness report).
Postwar South Norwood
1951 Apsley Road Playground opened by Croydon council.
1953 Croydon Sports Arena off Albert Road opened.
Central Cinema renamed Rex Cinema.
1956 Rex Cinema closed down.
1957 Astoria cinema at 45 High Street closed down.
1959 Trolley buses discontinued.
1960 Steam trains at Norwood Junction depot.
1966 Albert Tavern in Harrington Road rebuilt in modern style
1968 South Norwood Library opened on the corner of Selhurst Road and Lawrence Road. Architect: Hugh Lea.
1971 Odeon South Norwood at 18-22 Station Road closed and later demolished.
1974 Woodside Brickworks, Dickerson Lane, closed down.
1983 Selhurst Park ground redeveloped. A Sainsburys supermarket was incorporated (which reduced terrace seating).
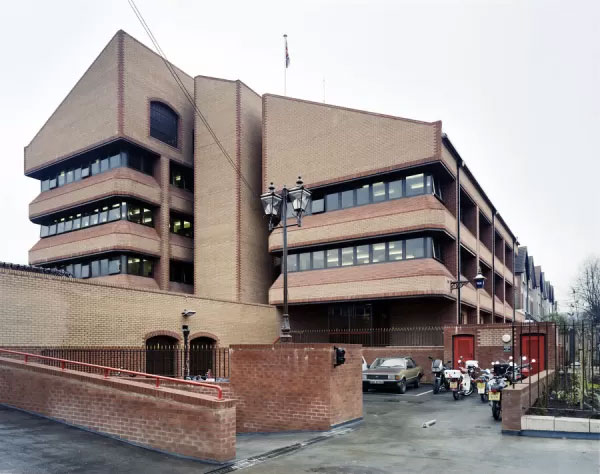
1987 South Norwood Police Station opened on Oliver Grove
1989 South Norwood Country Park opened. 116 acres. Entrance on Albert Road.
1990s Brickfield Meadow Park built on site of Woodside Brickworks, Dickerson Lane.
1994 Selhurst Park’s Holmesdale terrace demolished and replaced with a two-tiered 8,500 capacity stand.
1998 Harrington Road Station built for Croydon Tramline.
C21 South Norwood
2000 Arena stop opened as part of new Tramlink connecting Croydon with Beckenham.
c. South Norwood Islamic Centre opened at 3 Clifford Road.
2003 Goat House Hotel at 2-4 Penge Road closed and later demolished.
2007 The Gladstone pub at 167 Portland Road closed and converted to flats.
The Stanley Trade Technical School became Harris Academy South Norwood
2010 New London Overground service opened serving Norwood Junction.
2014 The Sensible Garden created by the local community. Named after Captain Sensible of The Damned who attended Stanley Technical School.
2017 South Norwood Police Station, on Oliver Grove, converted by Harris Academy Federation into a sixth form college for more than 200 local teenagers.
2021 Stanley Halls rebranded as Stanley Arts. Film of its history & future plans (6:50)
The Portmanor (ex-Signal) pub at 1 Portland Road converted to flats..
2022 The Ship, 55 High Street, closed down .
2024 Croydon Council re-approved the expansion of Selhurst Park football ground.
Further Reading:
The Great North Wood - J Corbet Anderson (1898)
The Phoenix Suburb - Alan R. Warwick ((1972/RP 2009 Norwood Society)
Norwood Past - John Coulter (1996 Historical Publications)
The Wood That Made London - C.J. Schüler (2021 Sandstone Press)